Finding BSCW objects
BSCW’s built-in search engine helps you find objects on your BSCW server. You specify your search in the ‘Edit Query’ form of a BSCW search.
• The ‘Search’ field contains the name of the folder where the search is to start. If you have numerous objects in many workspaces, try to limit the search to the most promising folder and avoid a time consuming search ‘in your workspaces’ – due to a time-out of your Web browser, your BSCW session could be aborted.
• The ‘for type’ field determines the type of object you are looking for (document, folder, etc.); choose ‘any’ if you don’t know the type.
• The rest of the form is about the search criteria that are to be matched by the objects you are looking for.
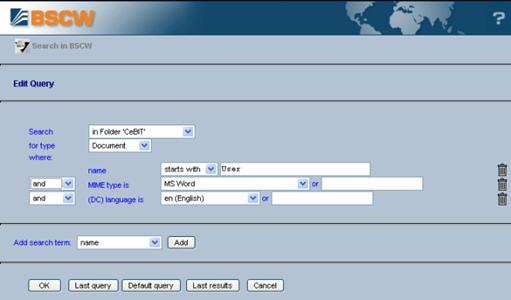
Figure 16: BSCW search form
The search criterion listed by default is the name of an
object. Other criteria may be added such as ‘content’, ‘description’, etc., also
including user-defined attributes. Select a
criterion from the ‘Add search term’ field and click [Add]. You can remove a
search criterion again by clicking on the  icon to its right.
icon to its right.
With many search criteria, you may determine how the search
phrase entered is to be used in searching. If you, e.g., choose ‘starts with’
and enter ‘About B’ into a name field, all objects will be found having a name
that starts with this phrase, e.g. ‘about BSCW’, ‘About being alone’. If you
select ‘<regex>’ instead of ‘starts with’, you may enter a regular
expression according to the Python regular expression syntax into the search
field. This is a feature for users familiar with Python regular expressions
(consult the Python Library Reference, module re). Note that input
in a tag search field is not interpreted as a phrase, but as a number of words
separated by blanks. If you choose ‘starts with’ and enter ‘sys rail’ into a
tags field, all objects will be found that have at least two tags assigned
starting with either ‘sys’ or ‘rail’, e.g. ‘railway’, ‘system’ or ‘Sysiphos’,
‘railing’.
Search criteria are combined to form more complex queries by using ‘and’, ‘or’, ‘and not’ and ‘or not’. The operators ‘and’ and ‘and not’ have higher priority than ‘or’ and ‘or not’, i.e. a query ‘A and B or C’ is interpreted as ‘(A and B) or C’.
When the indexing service PyLucene is in use on your BSCW server, not only the contents of documents will be indexed for a quicker search in your documents, but also object metadata like names, descriptions or tags. In this case, your input in search fields will be interpreted as words to be contained in the attributes of objects to be found. You may use wildcard characters in words and may also enter phrases enclosed in double quotes.
You may return to the [Default query] (which has ‘name’ as only search term) or the [Last query] executed.
BSCW will display the search result (i.e. the list of hits) as a folder listing. The description of each object names the folder that contains the object. Make sure that you have activated the option .
Please note that content-based search for documents (full
text search) is only possible for plain text and HTML documents (MIME type
text/plain and text/html) if no indexing service has
been installed with your BSCW server. In any case, a ‘content’ search criterion
is only applied after the other search criteria have been evaluated.
So, if you are only looking for documents based on content and your BSCW
installation offers an indexing service, you should use the search ‘In your
documents’ described below.